A Red Giant Has Which of the Following
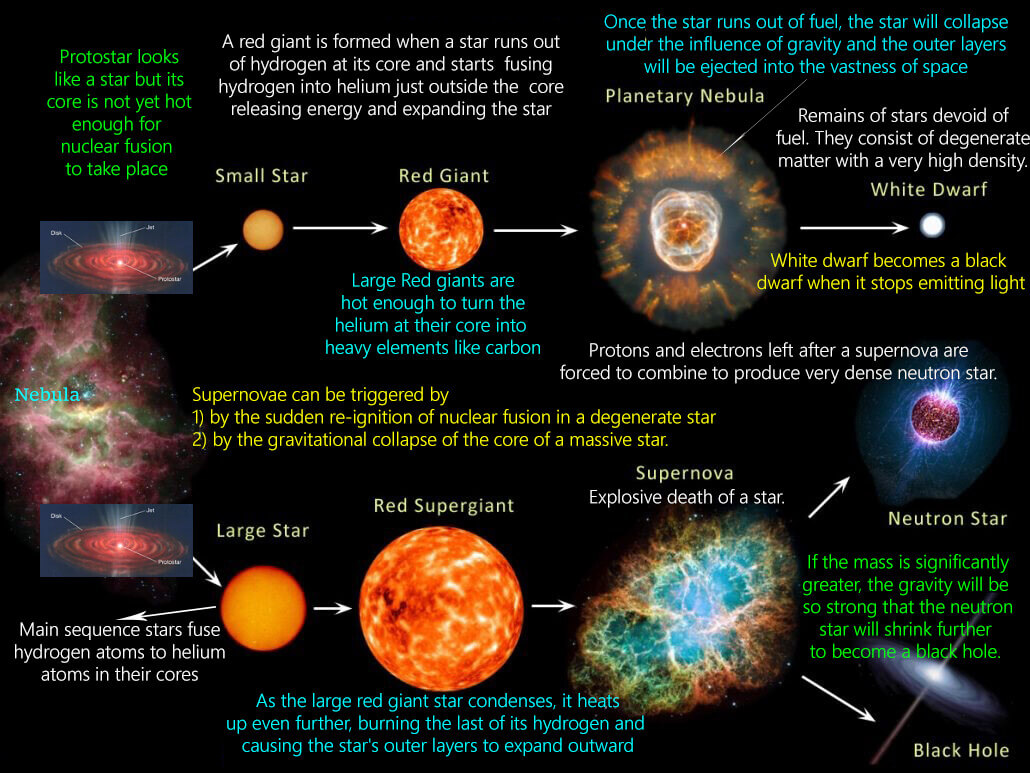
Contracting cloud of gas and dust protostar main-sequence G star red giant planetary nebula white dwarf. Rank the stages based on when they occur from first to last.
A red giant stars appearance is usually from yellow-orange to red including the spectral types K and M but also S class stars and carbon stars.
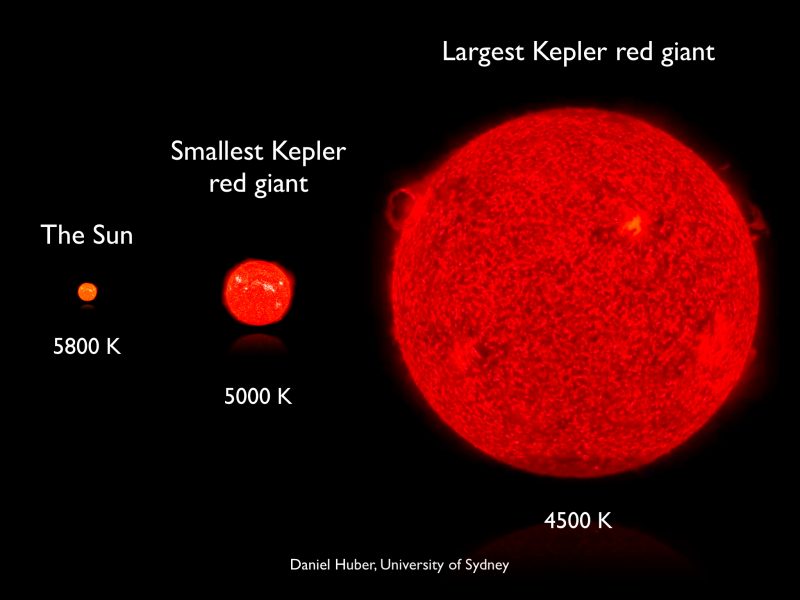
. Which type of fusion occurs in the red giant phase of the demise of a sunlike star. Once at the red giant stage a star might stay that way for up to a billion years. It has a mass of roughly half the mass of the Sun.
Question 48 A red giant has which of the following. The more massive the star is the faster it burns its fuel D. Have higher core temperatures.
The Red Giant is more luminous than the Main Sequence star. The amount of mass a star has determines which of the following life cycle paths it will take after the red giant phase. High mass stars evolve more rapidly than low mass ones because the high mass stars a.
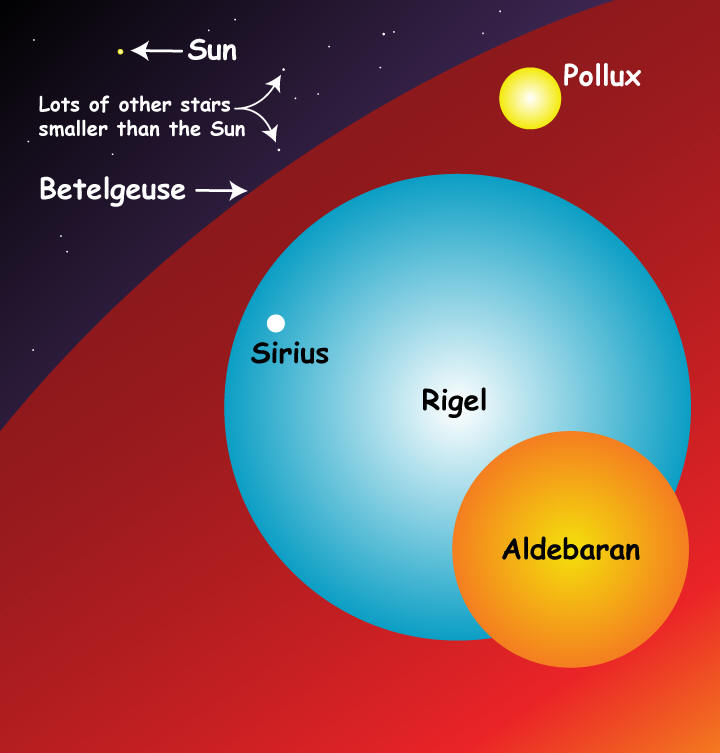
The Red Giant has a smaller radius than the Main Sequence Star. Which of the following has the longest life. Which of the following is true for Red Giant with the same surface temperature as a Main Sequence star.
No elements heavier than iron can be produced in a massive star. A red giant star is a dying star in the last stages of its stellar evolution. Which type of telescope would you need to easily see a potential.
The following figures show various stages during the life of a star with the same mass as the Sun. The stellar remnant of a one solar mass star is a a. It is made up mostly of hydrogen and helium.
The Red Giant is less luminous than the Main Sequence star. Question 51 Which of these is NOT a feature of white dwarf stars. The Red Giant is redder than the Main Sequence star.
Helium to carbon helium to hydrogen hydrogen to helium hydrogen to carbon. The star has now reached the red giant phase. Which of the following stars will live the longest.
Red giant stars usually result from low and intermediate-mass main-sequence stars of around 05 to 5 solar masses. A red giant is a star in its death stages. A gas cloud which goes into the formation of red giants.
Which of the following statements is FALSE. Have higher core densities. All stars evolve the same way up to the red giant phase.
It has slowly swollen up to many times its original size. A 1 solar mass star. O a non-fusing carbon core O a radius comparable to the Sun a.
The core of red giant star is made up of carbon B. Dwarf star sun. Its radius is about the same as the Earth.
A red giant is a luminous massive star that is in a late phase of stellar evolution. It is red because it is cooler than it was in the main sequence star stage and it is a giant because the outer shell has expanded outward. Red giant stars are normal main sequence stars that are formed due to the loss of their hydrogen supply which causes their outer layer to become inflated and to expand hugely and their surface temperature to reduce to as low as 5000 K.
Red giant stars have an intermediate or low mass. A red giant star is a dying star in the last stages of stellar evolution. The average star has shorter life span C.
Our own sun will turn into a red giant expand and engulf the inner planets possibly even Earth.

Types Of Stars Stellar Classification Lifecycle And Charts

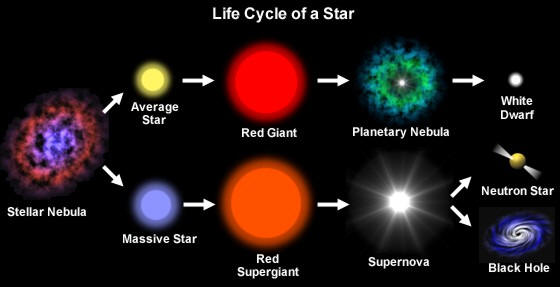
Star Formation Stellar Evolution Or Life Cycle Of A Star Pmf Ias
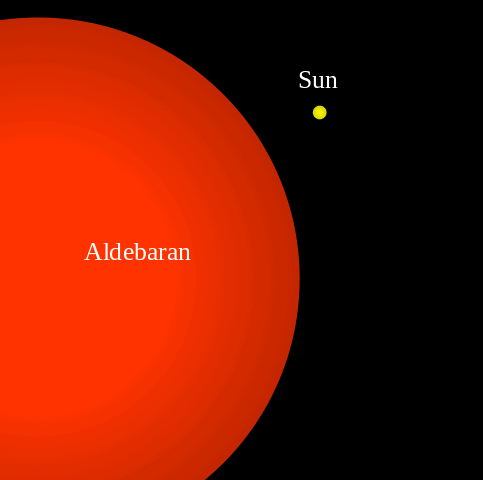
Red Giant Star Facts Information History Definition
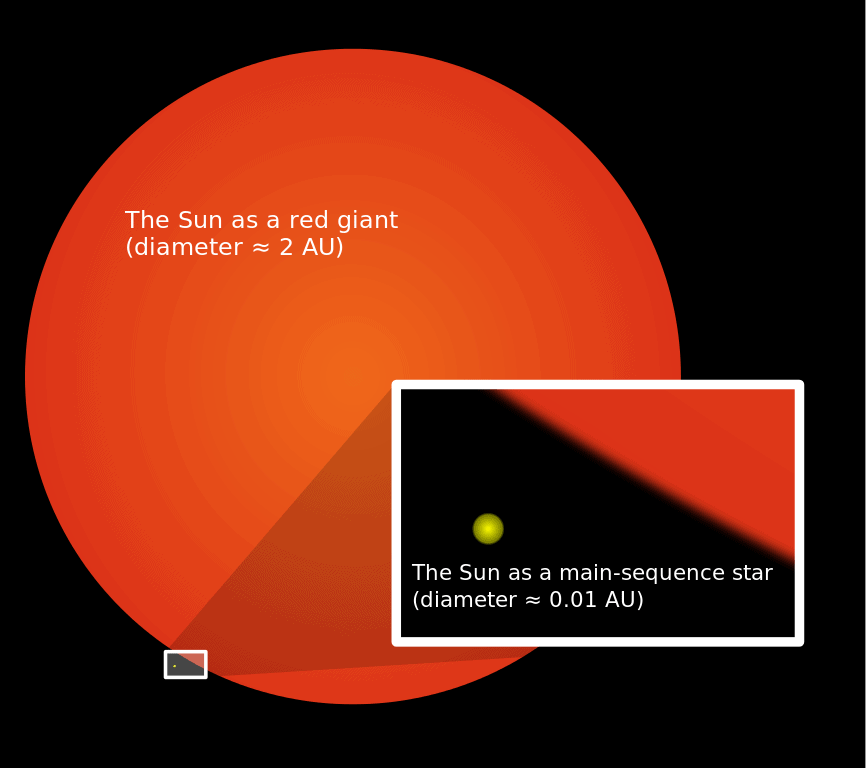
Red Giant Star Facts Information History Definition

Evolution From The Main Sequence To Red Giants Astronomy
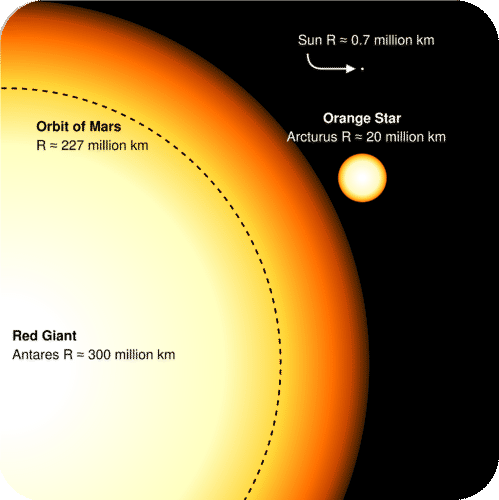
Life Cycles Of Stars Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation
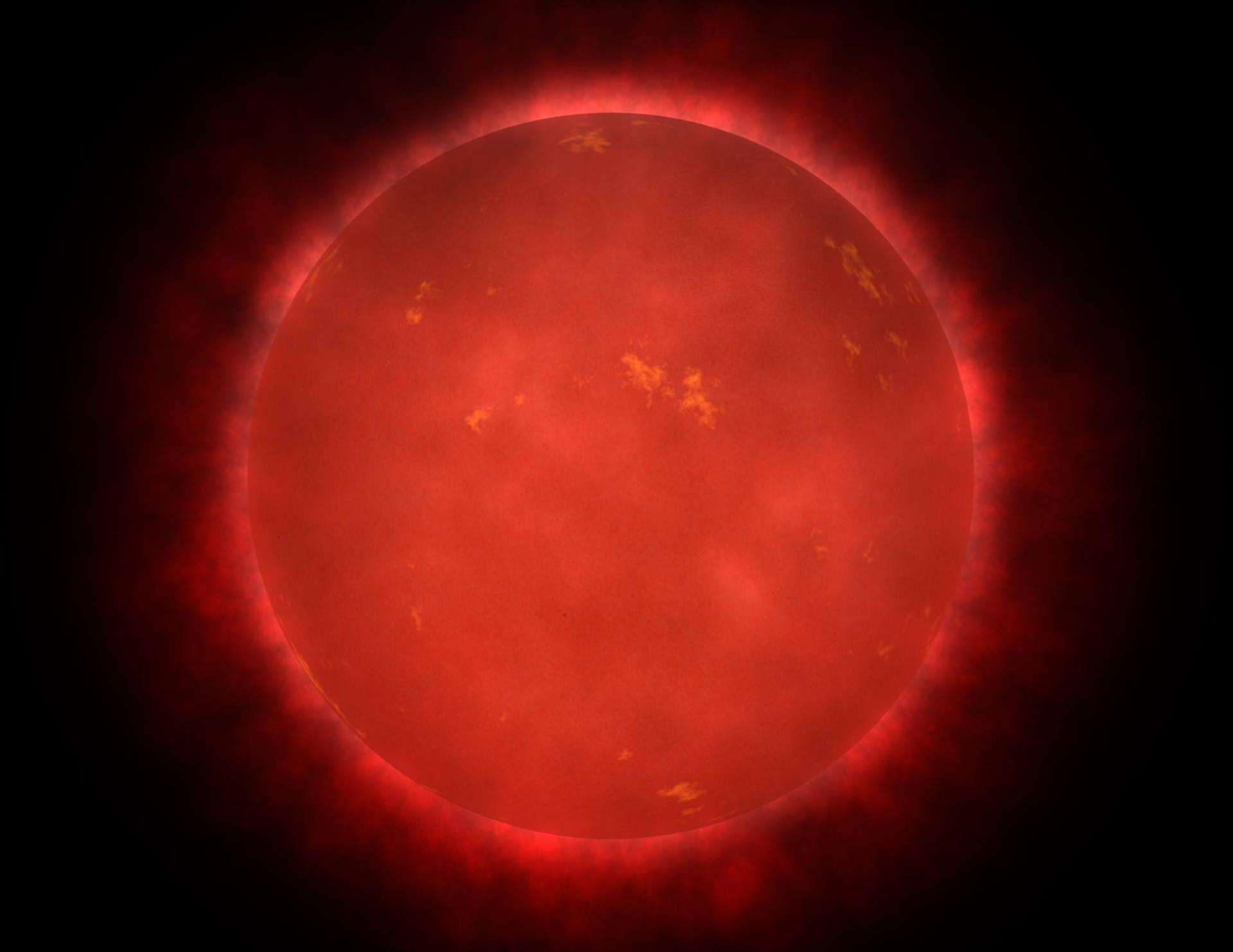

Red Giant Star Facts Information History Definition
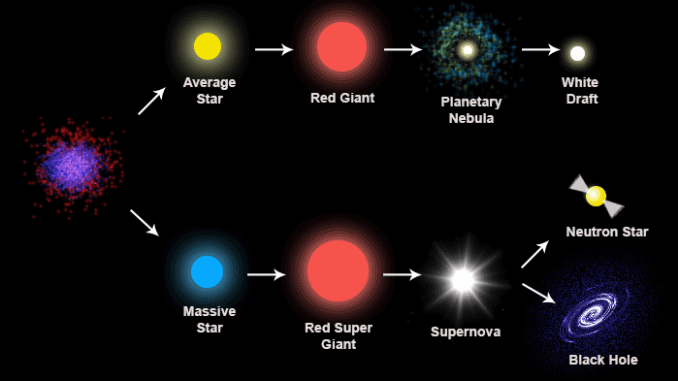
Red Giant Star Facts Information History Definition

Evolution From The Main Sequence To Red Giants Astronomy
Stars Low Mass Stellar Evolution



Comments
Post a Comment